Aim:
To check the quality of bricks regarding (i) Size, (ii) Shape, (iii) Colour, (iv) Hardness and Soundness (v) Density as per IS: 1077-1992, 3495-1992
Specifications:
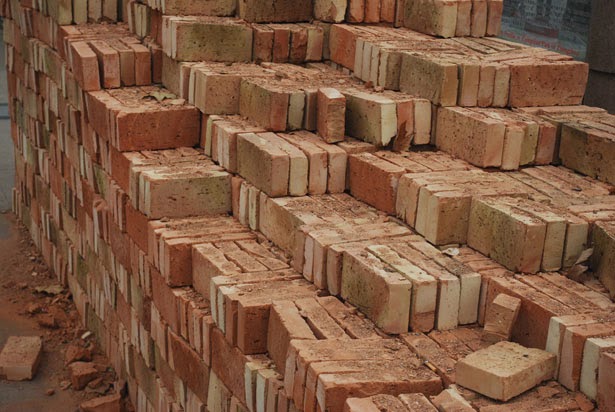
Size : The standard size of common building bricks traditionally used in West Bengal (248 mm x 121 mm x 70mm) and modular bricks 190 x 90 x 90 mm. Usually the length of bricks should be twice the width plus one mortar joint.
Shape : First class bricks should be truly rectangular in shape with smooth faces, straight and sharp edges. Edges should be at right angle at corners.
Colour : A well brunt-brick should be uniform ‘brick-red’ colour. A pale colour indicates under burning. A bluish colour indicates over burning.
Hardness and Soundness : First class bricks should have a fine compact and uniform texture. It should be hard, strong and durable. It should give a metallic sound when struck with a hammer or another brick. When dropped down from a height of one metre on another brick resting on ground it should not break. A freshly fractured should not show any cracks, fissures, hole, lump or pebbles etc.
When scratched with a finger nail, if no impression in left on the surface, the brick is assumed to be sufficiently hard.
Density:
Find the density of brick taking mean weight and mean volume. Equipment:
Steel tape, metre scale, Try-square, balance, drying oven etc.
Procedure :
1. Take 20 whole bricks at random from the stack, and all blisters, loose particles of clay and small projections shall be removed.
2. Arrange 20-numbers of full size bricks lengthwise leaving no gap in between and measure the total length. Repeat the measurement three times and take the mean.Get the length of single brick by dividing the mean by 20.
3. Take three such measurements by keeping the bricks breadthwise. Find the breadth of single brick as before.
4. Likewise find the height of single brick by arranging heightwise.
5. Record the result in table No. 1.
6. Observe the faces, edges and colour of the bricks and note the observation.
7. Take one brick in your left hand and strike with a hammer or another brick and note the sound. Allow a brick to fall a height of 1 metre on another brick resting on ground and see if it breaks.
8. Break one or two bricks and examine for the texture.
9. Scratch the brick surface with thumb-nail, observe whether any mark is left on the surface.
Observation and Results:
Size :
Table I
Trials Trial -1 Trial-II Trial III Mean of 3 Mean of 20-bricks Remarks
Length
Breadth
Height
Final Size:
Shape : Condition of
(i) Faces –
(ii) Edges –
Colour:
Striking Sound : Emits metallic sound / Emits dull sound
Result of dropping from a height of one meter : Break / Does not break
Texture : Uniform and closely grained / Non uniform-existence of cracks, fissure, holes, lumps of lime, pebbles etc.
Hardness : Finger nail impression – yes/no
Follow MyCivil at :-